As a college student, you’ll quickly become familiar with the concept of grades. It’s a fundamental aspect of your academic life, and understanding how the college grading scale works is essential for both your short-term and long-term academic success. Your grades not only reflect your academic performance but also contribute to your GPA (Grade Point Average), which can have a significant impact on your graduation, career opportunities, and academic standing.
Navigating the grading system isn’t always straightforward, especially when you’re first entering college. Letter grades, GPA calculations, and the different academic benchmarks can all feel confusing at first. This blog post aims to break down everything you need to know about the college grading scale, from the letter grade system to how it translates into your GPA, and provide you with the tools to better understand your academic progress.
What is the College Grading Scale?
The college grading scale is used to assess and quantify students’ academic performance across courses and assignments. Though grading scales can vary by school or department, the majority of U.S. colleges use a standard letter grading system paired with a 4.0 scale for calculating GPA.
The grading system typically includes the following letter grades:
- A (Excellent): Represents outstanding performance.
- B (Good): Indicates above-average performance.
- C (Satisfactory): Reflects average performance.
- D (Poor): A passing grade, but below average.
- F (Failing): A grade that indicates failure to meet the course requirements.
Additionally, many schools use pluses (+) and minuses (-) to further refine these categories, which can slightly impact your GPA.
The exact percentage ranges for each letter grade can vary from school to school, but here’s a general breakdown:
- A: 90–100%
- B: 80–89%
- C: 70–79%
- D: 60–69%
- F: Below 60%
This grading system is crucial because it’s the foundation for calculating your GPA, which is a key metric of your academic performance. Now, let’s dive into how letter grades translate into GPA and why that’s important.
How Letter Grades Translate into GPA
Your GPA (Grade Point Average) is a numerical value that represents the average of all your grades. It’s calculated by assigning each letter grade a specific number, or grade points, on a 4.0 scale. This scale is used to standardize the evaluation of your academic performance and allows schools to compare students’ grades objectively.
Here’s how the letter grades typically convert into grade points:
- A (Excellent): 4.0 GPA
- A-: 3.7 GPA
- B+: 3.3 GPA
- B (Good): 3.0 GPA
- B-: 2.7 GPA
- C+: 2.3 GPA
- C (Satisfactory): 2.0 GPA
- C-: 1.7 GPA
- D+: 1.3 GPA
- D (Poor): 1.0 GPA
- D-: 0.7 GPA
- F (Failing): 0.0 GPA
Understanding the GPA Calculation
Your GPA is calculated by averaging the grade points you earn for each course, weighted by the number of credits that course is worth. For example, a 4-credit class in which you earn an A will contribute more to your GPA than a 1-credit class where you earn a B.
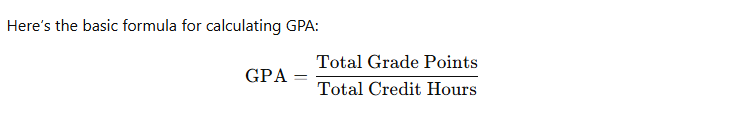
Let’s break that down further:
- Convert each letter grade to grade points: As shown in the chart above, you’ll assign the appropriate grade points for each class based on your letter grade.
- Multiply the grade points by the number of credits for each course: If you earned a B (3.0 GPA) in a 3-credit course, the contribution to your GPA would be 3.0 x 3 = 9.0 grade points.
- Add up all your grade points: Once you’ve multiplied your grade points by the credit hours for each class, add up all the grade points you’ve earned.
- Divide by the total credit hours: To get your GPA, divide the total grade points by the total number of credit hours you’ve taken.
For example, let’s say you took three courses in a semester: a 4-credit class where you earned an A, a 3-credit class where you earned a B, and a 2-credit class where you earned a C. Your GPA calculation would look like this:
- A (4 credits) = 4.0 GPA → 4.0 x 4 = 16.0 grade points
- B (3 credits) = 3.0 GPA → 3.0 x 3 = 9.0 grade points
- C (2 credits) = 2.0 GPA → 2.0 x 2 = 4.0 grade points
Total grade points = 16.0 + 9.0 + 4.0 = 29.0 grade points
Total credit hours = 4 + 3 + 2 = 9 credit hours
GPA = 29.0 grade points ÷ 9 credit hours = 3.22 GPA
The Importance of GPA in College
Your GPA is more than just a number; it’s a key factor in your college career. Here’s why it matters:
1. Academic Standing and Graduation Requirements
Each school has a minimum GPA requirement for graduation. Typically, students need to maintain at least a 2.0 GPA (a C average) to graduate. However, some programs, especially competitive majors or honors programs, may have higher GPA expectations. It’s also important to note that academic probation often begins if your GPA falls below a certain threshold, which could delay graduation or require you to improve your performance before continuing your studies.
2. Scholarships and Financial Aid
Many scholarships and financial aid programs have GPA requirements. To qualify for merit-based scholarships or maintain financial aid, students usually need to uphold a certain GPA. For example, some scholarships may require a 3.0 GPA or higher. Failing to meet these standards could result in losing financial support.
3. Graduate School Admissions
If you’re considering graduate school, your GPA will play a significant role in the admissions process. Competitive graduate programs, particularly in fields like medicine, law, and business, often have strict GPA requirements, sometimes requiring a minimum GPA of 3.5 or higher. However, GPA is just one factor in the admissions process—letters of recommendation, personal statements, and test scores are also considered.
4. Job Opportunities
Your GPA can also affect your post-college job search, especially for entry-level positions. Many employers look at GPA as a quick way to assess candidates’ work ethic, time management skills, and intellectual abilities. While your GPA isn’t the only factor employers consider, a strong GPA can help you stand out in a competitive job market.
What Are Plus and Minus Grades, and Why Do They Matter?
You may have noticed that many colleges use plus (+) and minus (-) grades in addition to standard letter grades. These grades add a level of precision to the GPA calculation, allowing for a more nuanced evaluation of your academic performance.
Here’s how the plus and minus grades typically affect your GPA:
- A+: Some schools consider an A+ as a 4.0 GPA, though this is not universal.
- A-: 3.7 GPA
- B+: 3.3 GPA
- B-: 2.7 GPA
- C+: 2.3 GPA
- C-: 1.7 GPA
- D+: 1.3 GPA
- D-: 0.7 GPA
While plus and minus grades have a relatively small effect on your GPA, they can still make a difference over time. For example, if you receive an A- in a few classes rather than a straight A, your GPA will be slightly lower. The cumulative effect of this over several semesters could impact your GPA more than you might expect.
Pass/Fail Grades and How They Affect Your GPA
In addition to the traditional letter grade system, many colleges offer students the option to take certain courses on a pass/fail basis. If you pass the course, you receive a “P” (Pass) on your transcript, which doesn’t affect your GPA. If you fail, you receive an “F”, which does impact your GPA like any other failing grade.
While pass/fail courses don’t contribute to your GPA positively, they also won’t drag it down if you pass. These courses can be useful for students who want to explore subjects outside their major or take classes that they might not be confident in. However, you should be cautious about overloading your schedule with pass/fail courses if you’re trying to improve your GPA.
Tips for Understanding and Managing Your GPA
- Keep Track of Your GPA Regularly: Regularly check your GPA, especially after each semester. Many universities provide online tools or GPA calculators to help students track their academic progress. Staying on top of your GPA will allow you to adjust your study habits or course load if necessary.
- Set Realistic GPA Goals: Based on your academic performance and career aspirations, set achievable GPA goals. If you’re aiming for graduate school, or want to qualify for certain scholarships, aim for a GPA of 3.5 or higher. If your GPA is lower than you’d like, consider what changes you can make to improve it.
- Use Your GPA Calculator: A GPA calculator is a great tool to help you predict how your grades will affect your GPA. By entering your current grades and the number of credits each course is worth, you can calculate your GPA at any given time during the semester. This will help you plan ahead and understand the impact of your grades.
Conclusion
The college grading scale and how it translates into GPA is essential for academic success. Your GPA reflects the effort you put into your courses and is a key factor in your college experience, from scholarships to job opportunities to graduate school admissions. By tracking your grades, setting academic goals, and using tools like GPA calculators, you can stay on top of your academic performance and make informed decisions about your studies.
With a clear understanding of the grading scale, you’ll be better prepared to manage your college journey, achieve your academic goals, and set yourself up for success after graduation. Remember, your GPA is just one measure of success—but understanding it and taking proactive steps to improve it will help you get where you want to go!

Leave a Reply